BUDDY User Manual
1. Introduction
Welcome to BUDDY!
![]()
BUDDY is an open-source cheminformatic software platform, capitalizing on bottom-up MS/MS interrogation and experiment-specific global peak annotation.
Bottom-up MS/MS interrogation aims to determine molecular formulae for all metabolic features with significance estimation. Experiment-specific global peak annotation aims to construct valid biotic or abiotic metabolic feature connections while refining individual feature annotations. For detailed methodology, please refer to our paper.
Wish you a wonderful journey in BUDDY!
2. Installation
BUDDY can be freely downloaded on this GitHub release page.
2.1 First-time installation
If this is your first time to install BUDDY on your PC, please do as follows.
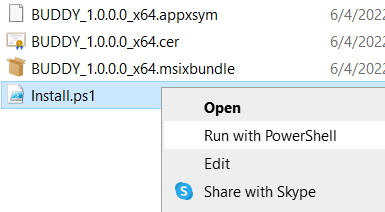
Unzip and open the downloaded file, right click the “Install.ps1” file and Run with PowerShell.
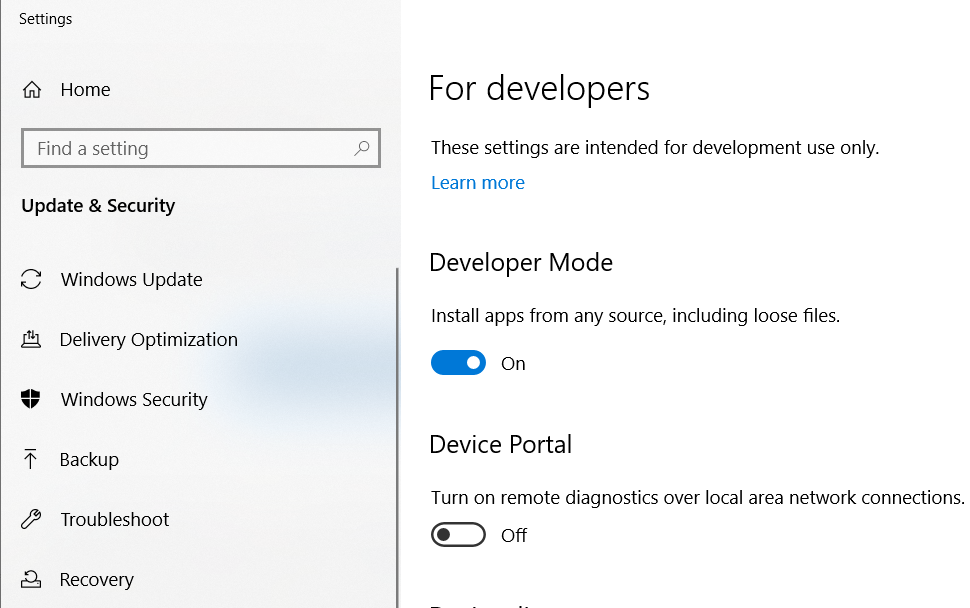
Press Enter. Once a pop-up window appears, then press Y. Meanwhile, you will be directed to enable the Developer Mode on your PC.
You are all set! BUDDY should appear in your start menu by searching for BUDDY!
2.2 Installation of an updated version
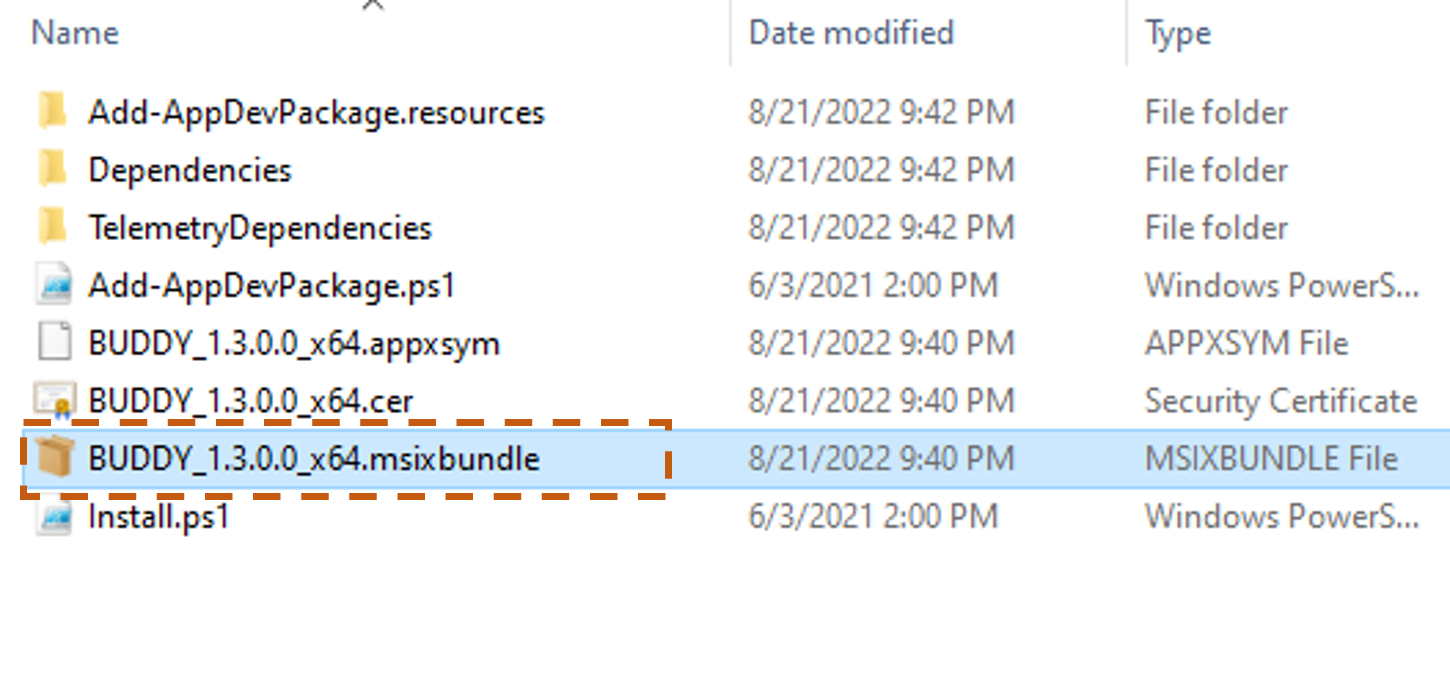
If you have BUDDY already installed on your PC and you are installing an updated version, please do as follows. Unzip and open the downloaded file, double click the “BUDDY_x.x.0.0_x64.msixbundle” file.
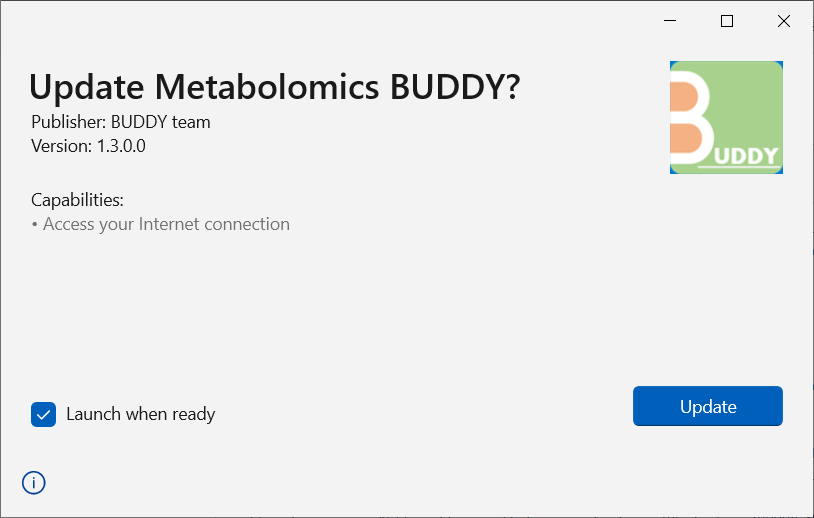
You will be directed to a window as below. Click Update, and you are all set!
3. Graphical User Interface
We offer an intuitive graphical user interface for BUDDY. A brief introduction of each panel is provided as below.
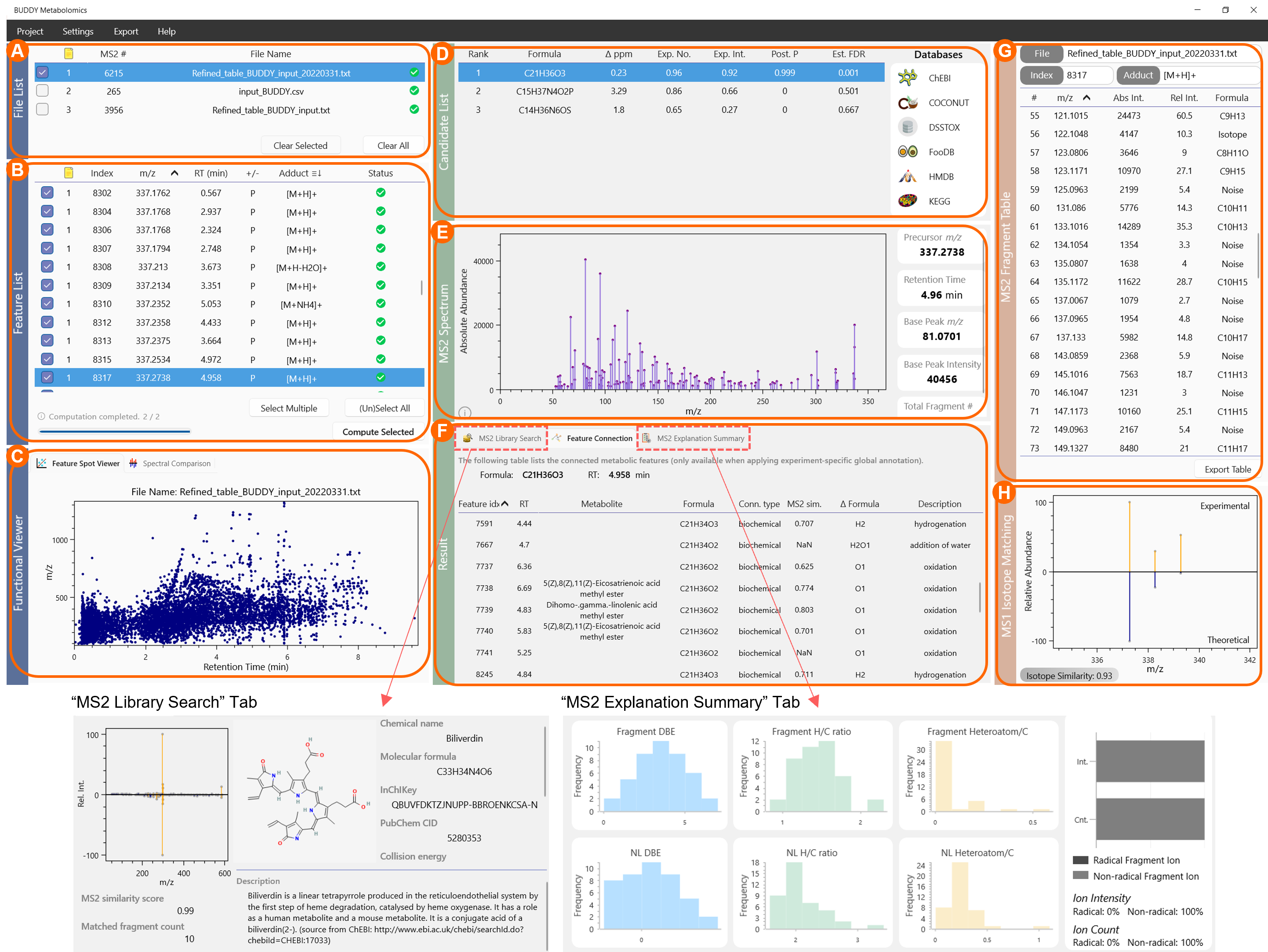
3.1 File List (panel A)
This panel contains all the imported files (single or batch import). You can check any file to show its metabolic features in the Feature List panel.
3.2 Feature List (panel B)
This panel contains all the metabolic features within the selected files. You can sort each column by clicking on the column name. You can redefine the adduct form for each feature by double clicking the adduct box. To check multiple features, highlight wanted features with Ctrl pressed, and click Select Multiple. To select or unselect all the features shown in the list, click (Un)Select All. During the computation, a progress bar will appear in the bottom left corner. After calculation, features labelled with the blue “S” are identified features (according to the set-up metabolite identification threshold).
3.3 Functional Viewer (panel C)
There are two panels in the Functional Viewer. Feature Spot Viewer and Spectral Comparison. Feature Spot Viewer offers a scatter plot in the m/z-RT domain. It shows the all the feature spots within the selected file in the File List. Spectral Comparison provides a straightforward panel to directly compare two MS/MS spectra. Users can simply drag features with MS/MS from the Feature List and drop them here for spectral comparison. In practice, this allows users to quickly check whether two MS/MS are of the same identity or any structural relation.
3.4 Candidate List (panel D)
This panel lists the formula candidates together with their basic information including mass deviations, explained fragment counts & intensities, estimated posterior probabilities and FDRs. Users can highlight each formula candidate to see their corresponding MS/MS explanation quality in the Result panel. The Databases list in the right shows in which chemical databases this formula can be found.
3.5 MS2 Spectrum (panel E)
This panel shows the original MS/MS spectrum and some metadata. Users can left click on the peak apex to show m/z & abundance. Hold right click to adjust the spectrum axis range. Double click the scroll wheel to restore the default view.
3.6 Result (panel F)
There are currently three panels within the Result module. MS2 Library Search is available for seed metabolites (or identified metabolites), showing mirror plots of MS/MS matching and detailed introductions of the identified molecule. Molecule descriptions are mirrored from PubChem using its API, allowing users to perform manual inspections more conveniently. Feature Connection panel is available when the experiment-specific global annotation task is performed. This panel lists all the metabolic features that are connected to the selected feature and their connection types. MS2 Explanation Summary summarizes how the selected formula candidate explains the target MS/MS spectrum in terms of double bond equivalent (DBE) values, hydrogen / C ratios, heteroatom / C ratios and radical fragment ions. These evaluation metrics can be essential to the candidate ranking process.
3.7 MS2 Fragment Table (panel G)
This panel lists all the fragment ions and their subformula annotations. In case that some fragment ions are not annotated within the first-round search, users can apply MS2 Fragment Reannotation in Others in the advanced settings. The fragment table is sortable.
3.8 MS1 Isotope Matching (panel H)
If MS1 isotope pattern is used for annotation, a mirror image of experimental MS1 isotope and theoretical isotope pattern will be shown here. The detailed MS1 isotope similarity algorithm can be found within the supplementary information of our paper.
4. Data import
BUDDY provides both single query import and batch import.
4.1 Single import
For single query import, BUDDY offers a pop-up window (Menu: Project - New (Single search)). Users can click on the Demo data to see the input format. At least one of the MS1 isotope and MS/MS spectrum is required for the following annotation.
4.2 Batch import
BUDDY accepts various formats of batch query import, including metabolic feature tables (output by MS-DIAL or custom tables as indicated), mzML files and MGF files. To import batch queries, go to menu: Project - New (Batch search).
4.2.1 Import from feature table
If you are using MS-DIAL for data preprocessing, you can directly import metabolic feature tables output by MS-DIAL (in txt format) into BUDDY. Specifically for feature tables output by MS-DIAL, we offer an addition step of metabolic feature clustering to remove redundant features, which can be set up in the advanced settings.
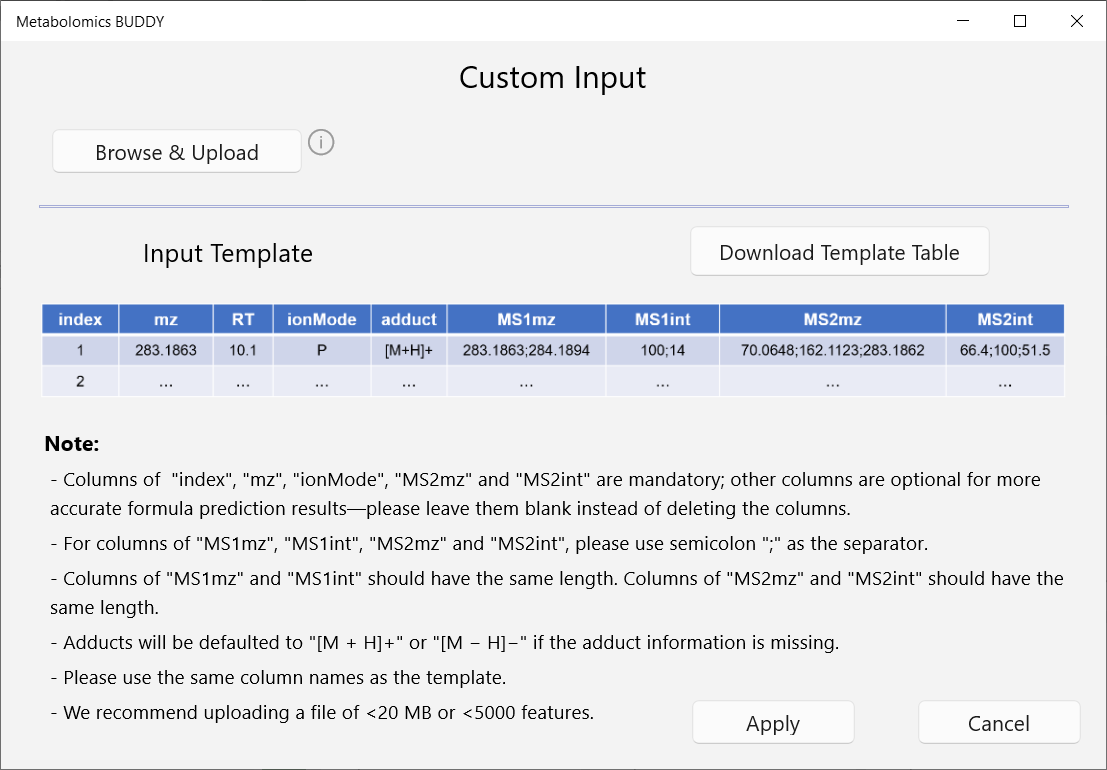
Otherwise, we also provide a custom feature table format (in csv). A template table is downloadable in the pop-up window. Please follow the instructions carefully.
4.2.2 Import from mzML or MGF file
You can directly import mzML files containing raw data into BUDDY for downstream analysis. At this stage, we only accept data-dependent acquisition (DDA) data and automatically reserve metabolic features with MS/MS collected. Adjacent MS/MS will be grouped by default using the cosine similarity. MS1 isotope patterns will also be extracted. You can change the relevant parameter details in the advanced settings.
MGF files containing multiple MS/MS spectra can also be directly imported into BUDDY. Every MS/MS will be treated separately, and no additional MS/MS grouping is performed.
5. Settings
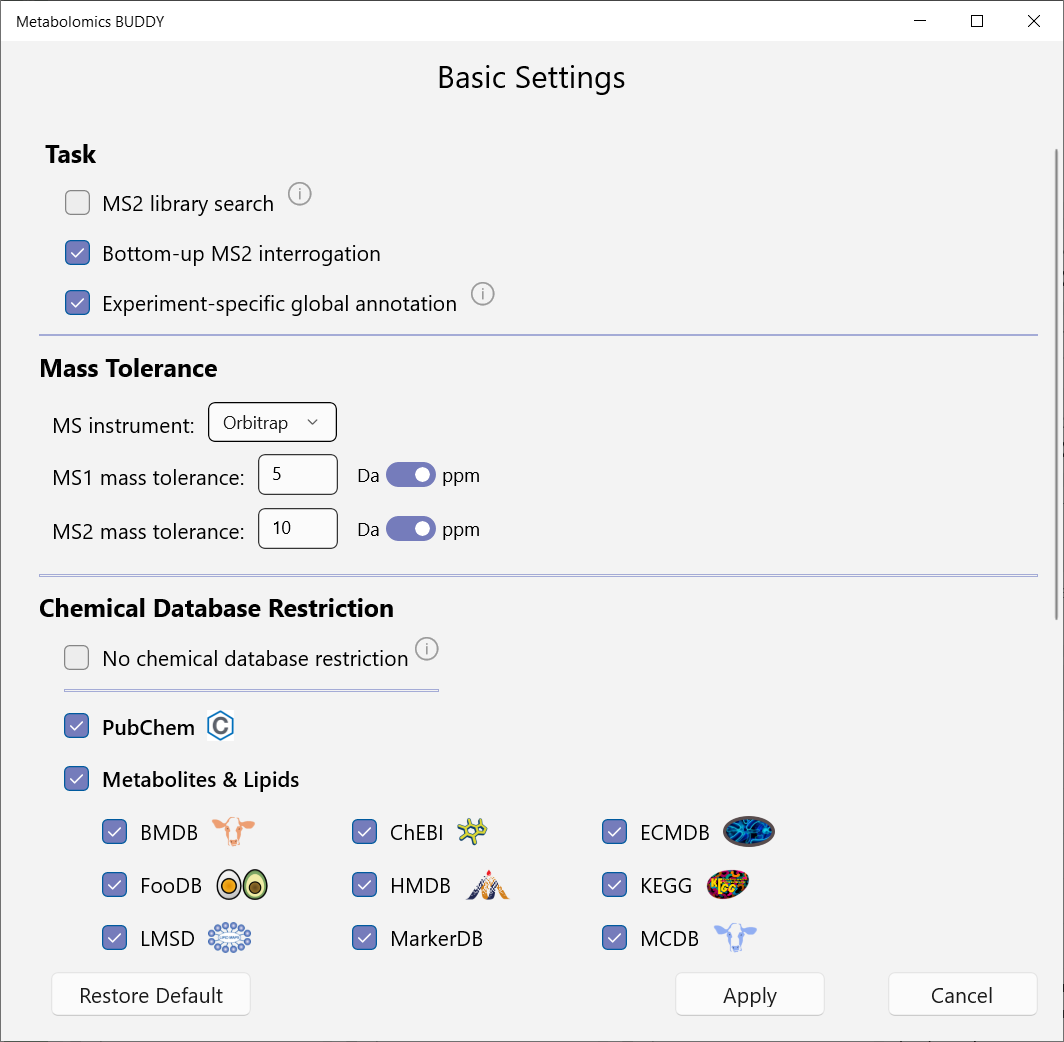
5.1 Basic settings
Basic Settings is a simplified version of Advanced Settings, allowing users to change the most important parameters at the first convenience (Menu: Settings - Basic).
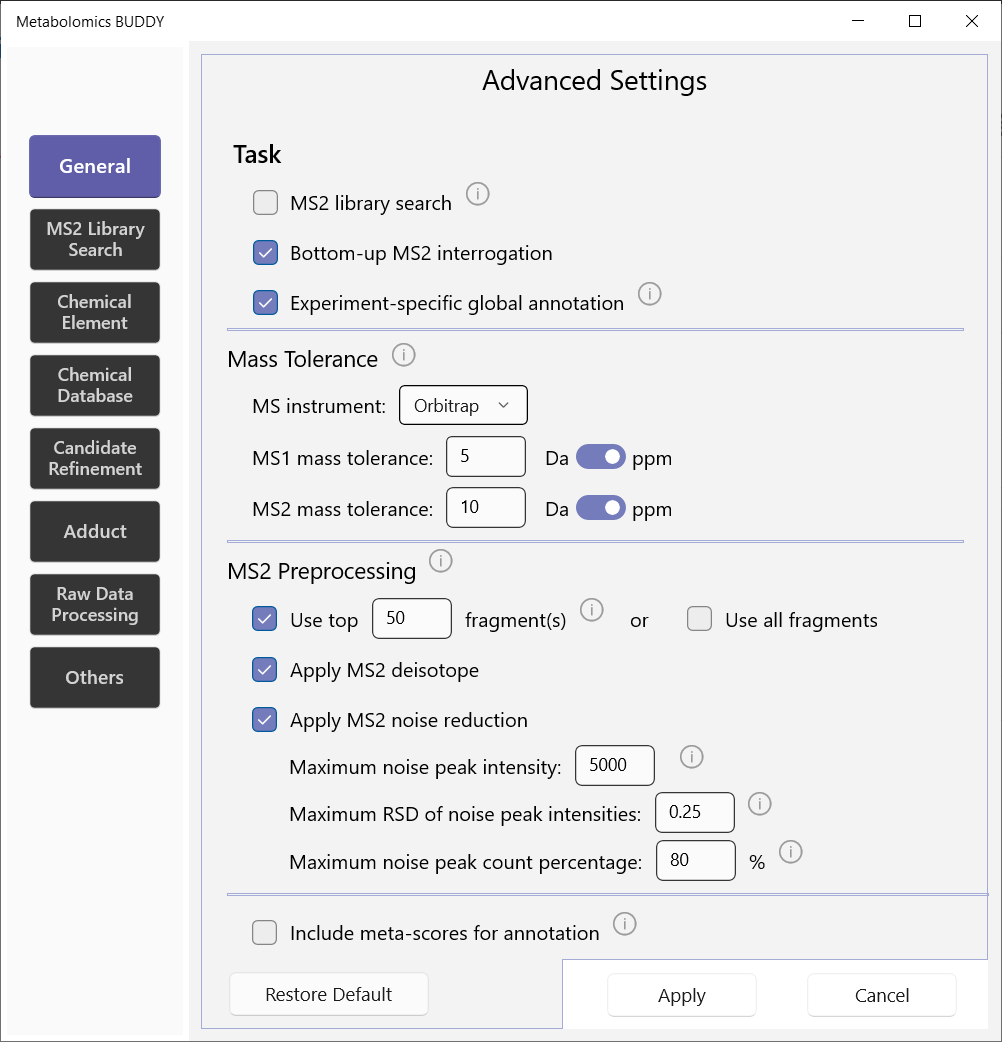
5.2 Advanced settings
To access all the settings, go to menu: Settings - Advanced.
5.2.1 General
BUDDY is able to perform three tasks as shown below. Experiment-specific global annotation must be performed together with Bottom-up MS2 interrogation. Notably, users can choose to apply meta-score inclusion for annotation, which uses metadata of molecular formulae in chemical databases. This could improve the annotation rate for known formulae at the cost of potentially missing discovery of novel molecular formulae.
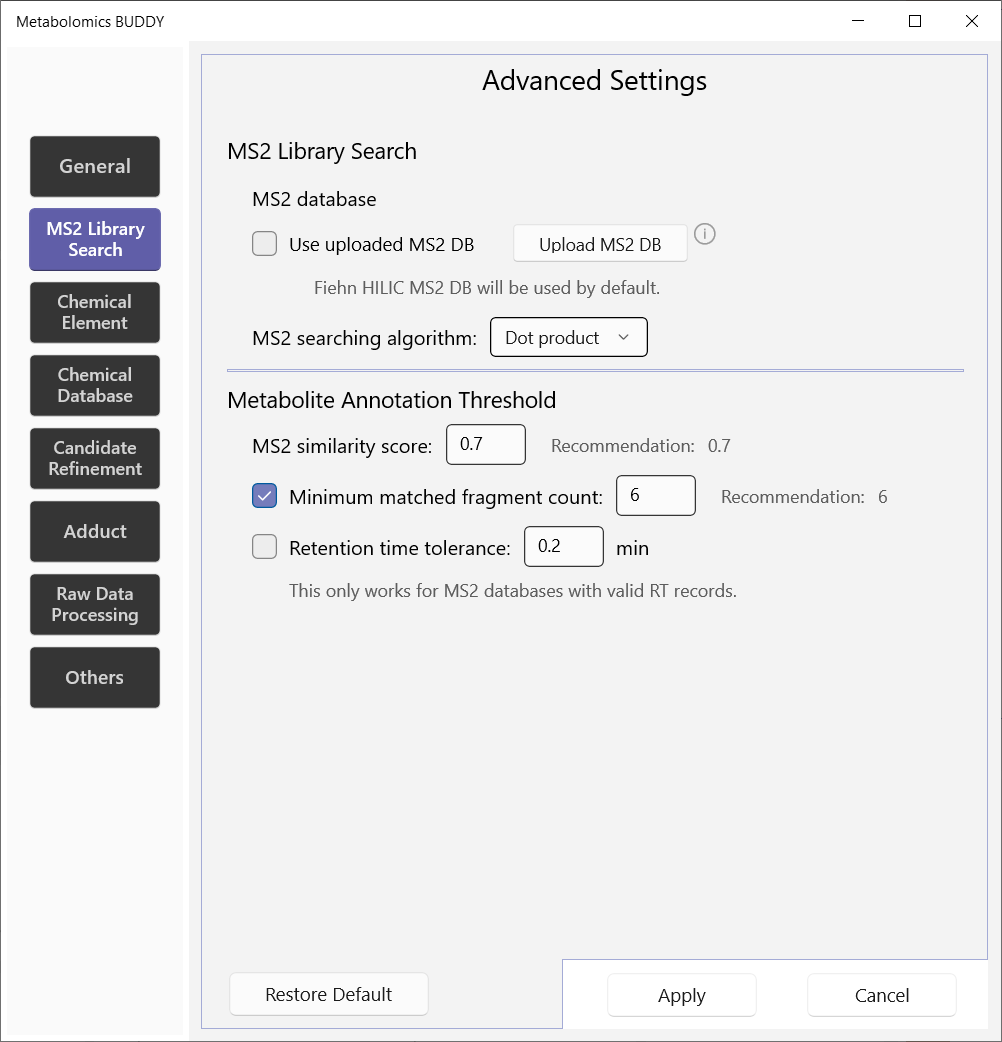
5.2.2 MS2 library search
Users can upload their own spectral libraries in msp format for metabolite identification. By default, the Fiehn HILIC library will be used. We provide three MS/MS searching algorithms—dot product, reverse dot product and spectral entropy similarity. Users can customize metabolite annotation thresholds on MS/MS similarity score, minimum matched fragment count and retention time matching.
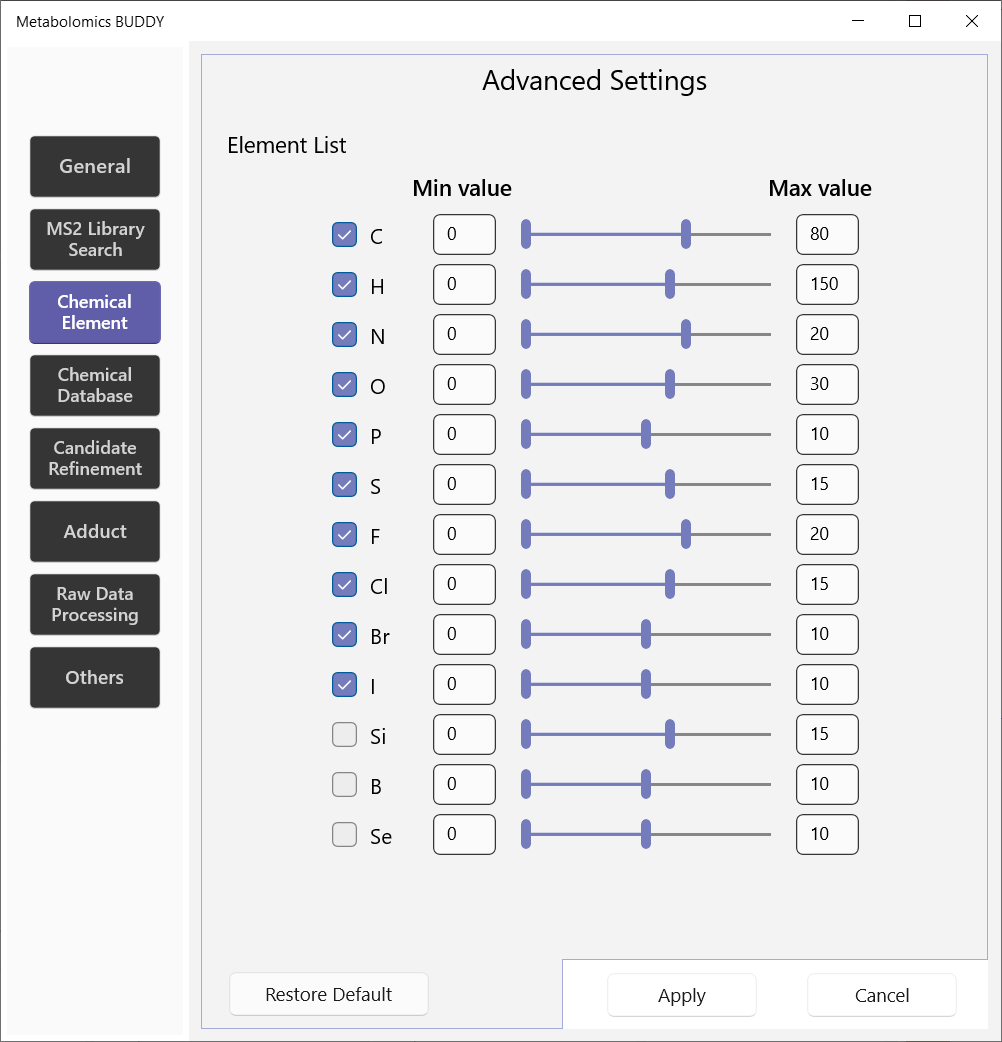
5.2.3 Chemical element
Users here specify the chemical elements that are allowed for formula annotation. The recommended max values are provided according to the reference.
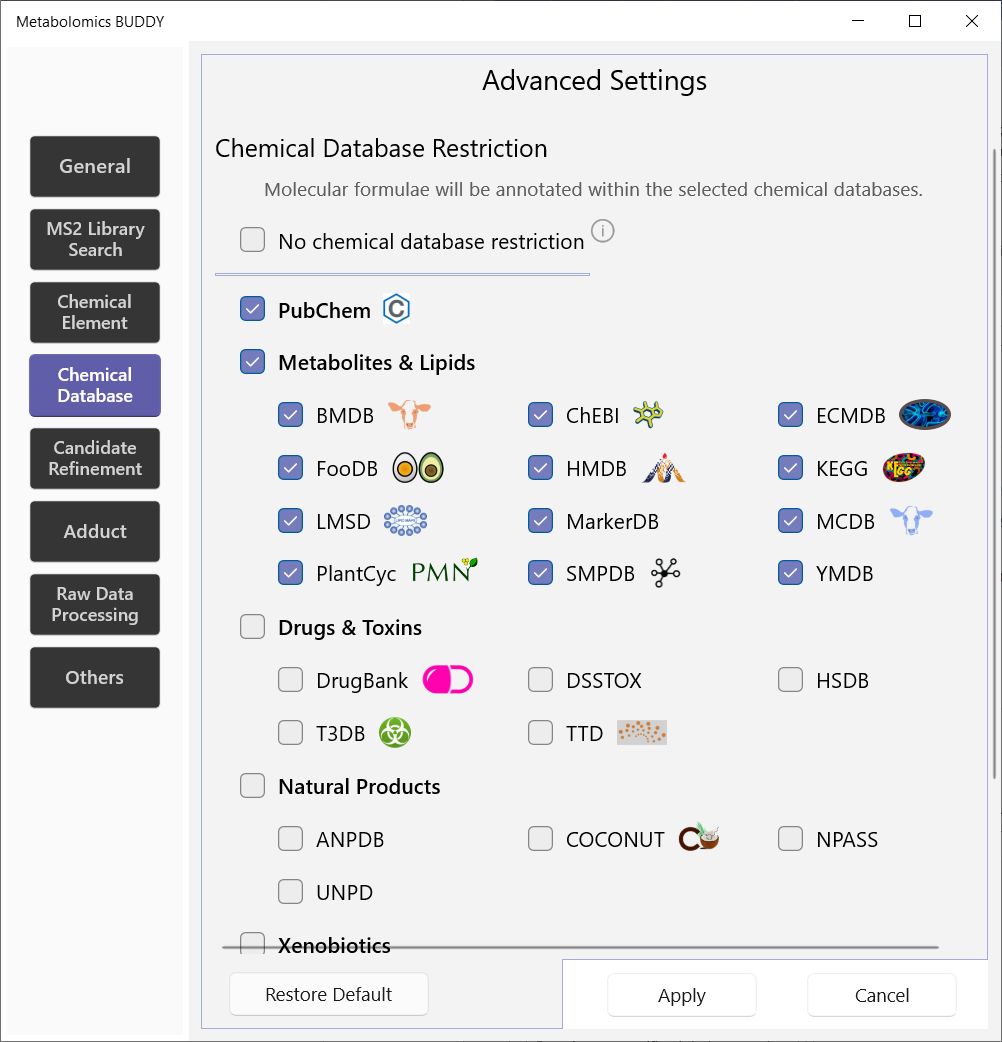
5.2.4 Chemical database
Users here specify the chemical databases in which formulae should be searched. If users do not want to apply any database restriction, No chemical database restriction should be checked.
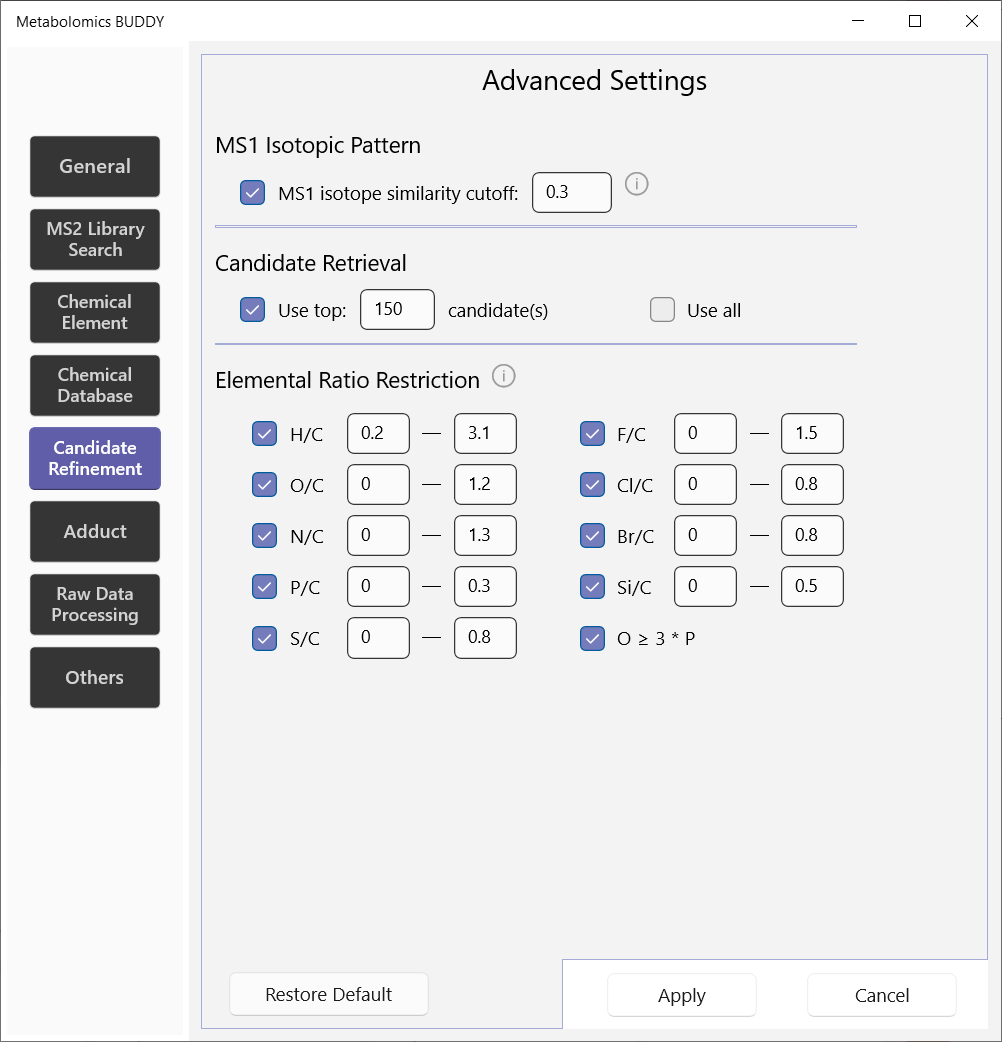
5.2.5 Candidate refinement
This page of settings helps to further refine formula candidates in terms of MS1 isotope pattern and elemental ratios. Elemental ratio restrictions are set up as summarized in the reference.
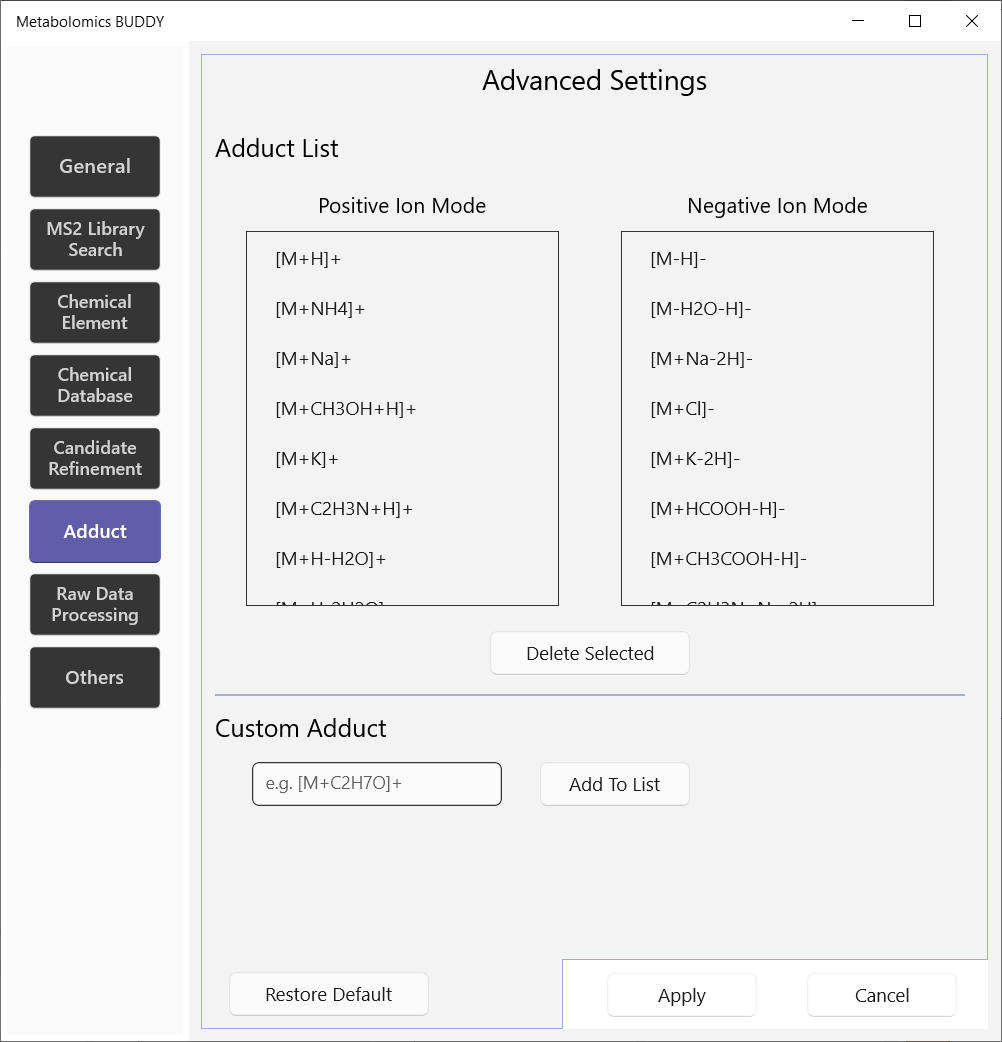
5.2.6 Adduct
We provide a list of 16 adduct forms in positive ion mode and 14 in negative ion mode. Users are allowed to add custom adducts.
5.2.7 Raw data preprocessing
If you are importing metabolite feature tables from MS-DIAL, we are able to conduct additional step of metabolic feature clustering for the features representing the same metabolite. This can avoid redundant annotation process.
For mzML file import, you can customize the data preprocessing on MS1 isotope and MS/MS grouping. MS/MS acquired within the maximum peak width window are grouped together if they share a cosine similarity score above the cut-off value. MS/MS merging will automatically merge the MS/MS spectra of the same identity.
5.2.8 Others
A timeout setting is offered to cease the computation process on a single query. You can choose to reannotate the subformula information in case that some fragments remain unexplained in the first-round search.
6. Export results
To export results, go to menu: Export.
6.1 Export single query
Export Single Query exports the annotation for a single metabolic feature query, where all the formula candidates and their separate MS/MS explanations are output.
6.2 Export batch results
To export batch results, we offer two options, Export Batch Summary and Export Detailed Results.
Export Batch Summary will export a single csv file containing all the features within the selected files, where the formulae ranked the highest will be output.
Export Detailed Results will export a zip file, containing annotation results of each file, each MS/MS, each formula candidate and each fragment ion in a hierarchical manner. It usually takes several minutes to Export Detailed Results for thousands of metabolic features.
7. Save and load BUDDY project
To save and reload the project space, users can save the current project in BUDDY as a BUDDY file and reload it back to BUDDY.
Save project: Menu: Project - Save or Save as.
Open project: Menu: Project - Open.